NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS
Nuclear Engineering Section
LOW LEVEL - LOW ENERGY (5-200keV) GAMMA SPECTROSCOPY
 The gamma spectroscopy analysis in the low energy region below 200 keV
is conducted using a Low Energy Germanium Detector LEGe with the
following specifications:
The gamma spectroscopy analysis in the low energy region below 200 keV
is conducted using a Low Energy Germanium Detector LEGe with the
following specifications:
Active area 2000 mm², Thickness 20 mm, 0.5 mm Be window
Resolution: 340 eV at 5.9 keV, 530 eV at 122 keV.
The samples analysed are usually of environmental origin, such as
soil, fly-ash, bottom-ash, building materials and water, with low
activity, thus the use of large sample volumes is necessary.
When analysing bulk samples using low energy photons, such as 46.52
keV (Pb-210), 59.54 keV (Am-241) and 63.29 keV (Th-234), the countrate
is highly affected by the intense self absorption of the low energy
photons, which is material dependent.
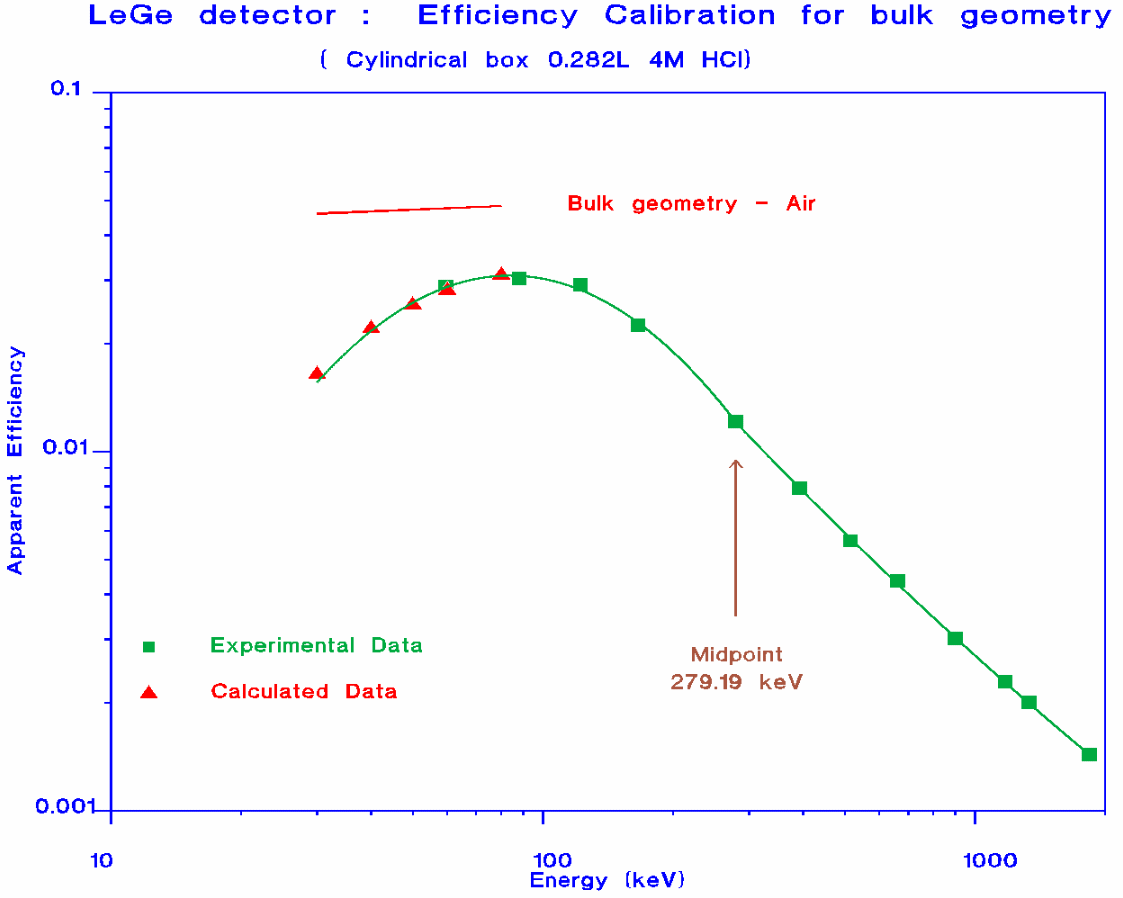
The efficiency calibration of the detector in the energy region
0-2000 keV is obtained using standard mixed radionuclide solutions.
The curve obtained is valid for the analysis of samples with the
same geometry (cylindrical box 0.282 L) and, especially in the low
energy region, the same material.
 The difference in the absorbing properties between the calibration
source and the sample requires the introduction of an efficiency
correction factor. A method ([15,1995])
which is applicable for any cylindrical
geometry was adapted for the determination of the above
correction factor, using a newly developed experimental-numerical
technique and a Fortran Program. This program using as input the
detector geometry, the source-to-detector distance and the linear
attenuation coefficients µ of both the calibration source and the
material to be analysed, calculates the efficiency correction
factor.
The difference in the absorbing properties between the calibration
source and the sample requires the introduction of an efficiency
correction factor. A method ([15,1995])
which is applicable for any cylindrical
geometry was adapted for the determination of the above
correction factor, using a newly developed experimental-numerical
technique and a Fortran Program. This program using as input the
detector geometry, the source-to-detector distance and the linear
attenuation coefficients µ of both the calibration source and the
material to be analysed, calculates the efficiency correction
factor.
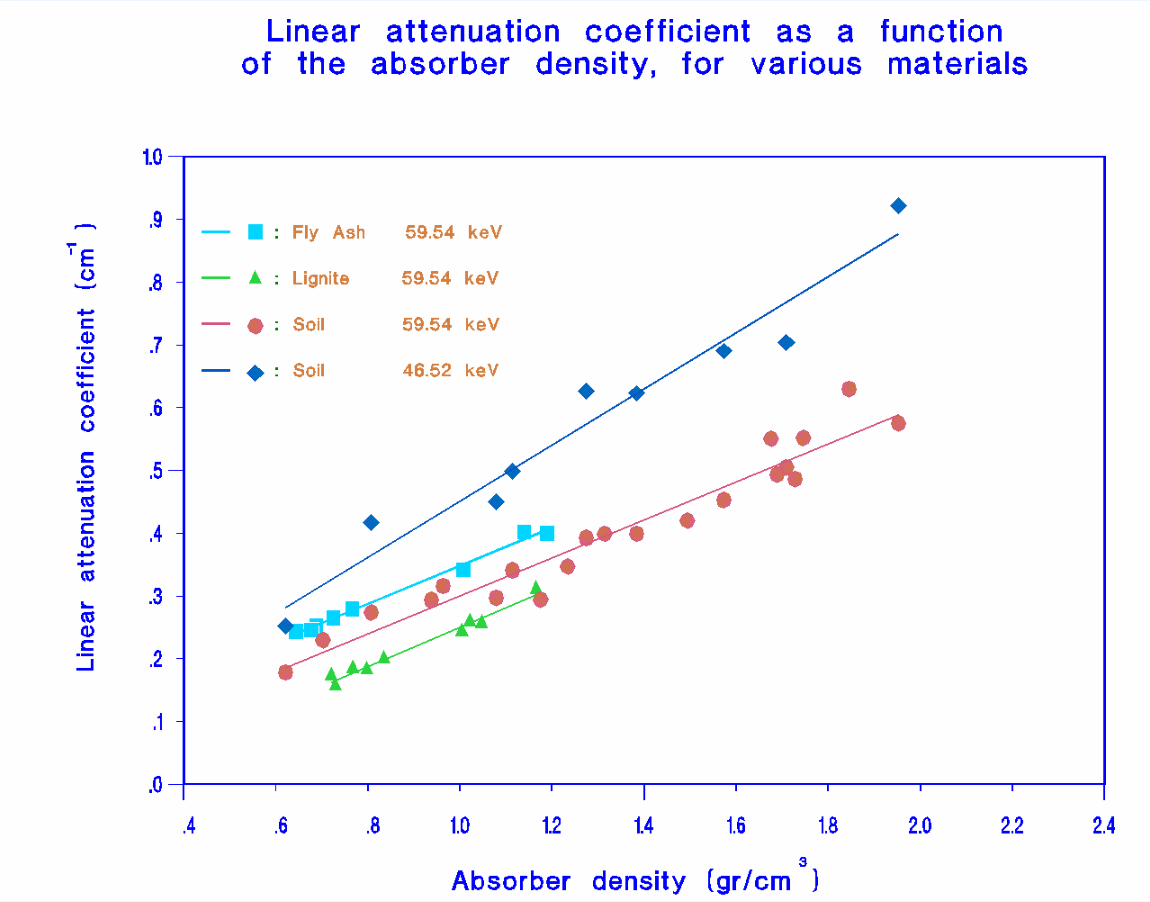
The values of the linear attenuation coefficient
needed for the above calculation are being experimentally estimated
for each material to be analysed. According to the results obtained,
in the case of surface soil, lignite and fly ash the values of µ
ranges from 0.2 - 0.9 cm¯¹, and leads to efficiency correction
factors between the calibration source and analysed material in the
range between 0.5 - 1.2, for photons with energies 46.52 and 59.54
keV. In the case of 185.99 keV photons, the efficiency correction
factor is slightly lower than 1.0, even for the most absorbing of
the materials analysed.
For the analysis of the collected spectrum the in-house developed UNIX-based
Computer Code SPUNAL is used.
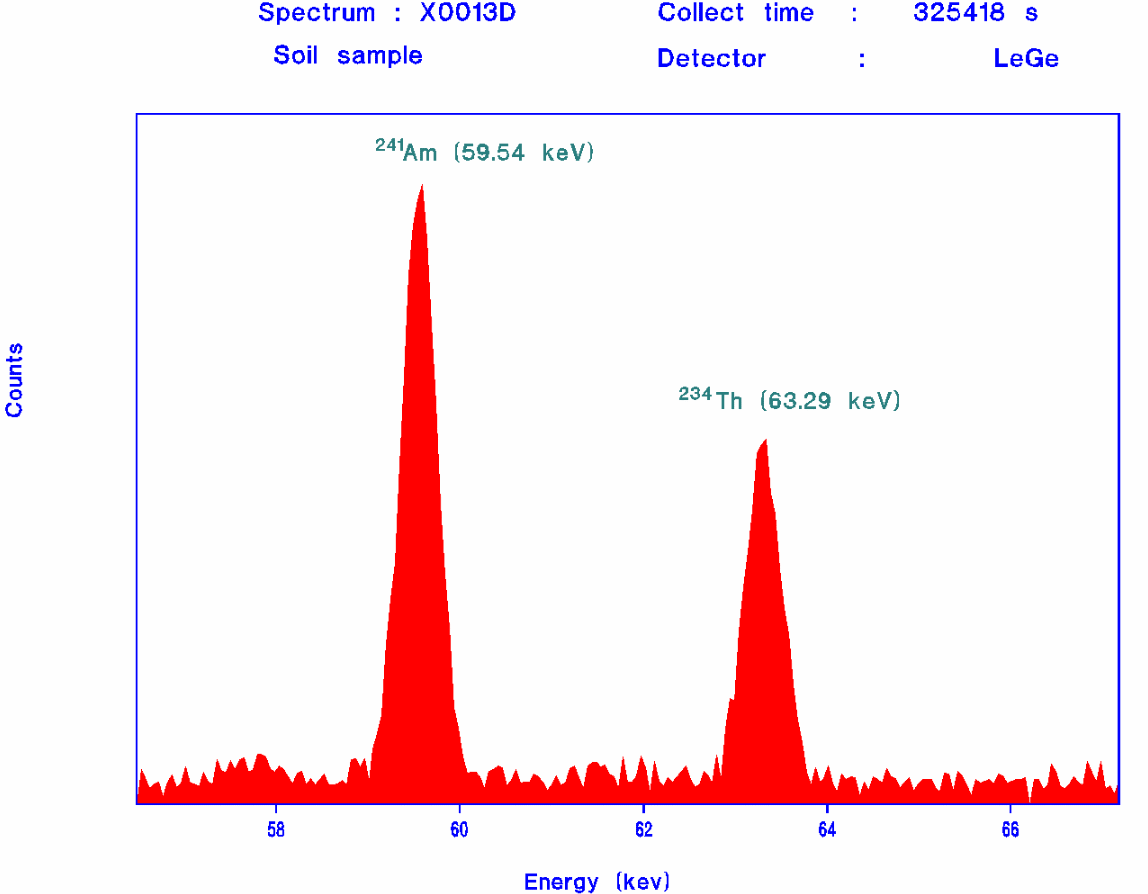
Among the isotopes identified in the soil samples analysed, was
Am-241 ([5,1989]).
The samples were collected in the aftermath of the Chernobyl
accident. Furthermore, Am-241 was identified in
air-filters collected in Athens in May 1986, and the maximum air concentration
was estimated to 8 mBq/m³ ([8,1991]).
The 63.29 photopeak in the air-filter sample is due to detector
background.

Back to the Previous Page
 The gamma spectroscopy analysis in the low energy region below 200 keV
is conducted using a Low Energy Germanium Detector LEGe with the
following specifications:
The gamma spectroscopy analysis in the low energy region below 200 keV
is conducted using a Low Energy Germanium Detector LEGe with the
following specifications:
 The difference in the absorbing properties between the calibration
source and the sample requires the introduction of an efficiency
correction factor. A method ([15,1995])
which is applicable for any cylindrical
geometry was adapted for the determination of the above
correction factor, using a newly developed experimental-numerical
technique and a Fortran Program. This program using as input the
detector geometry, the source-to-detector distance and the linear
attenuation coefficients µ of both the calibration source and the
material to be analysed, calculates the efficiency correction
factor.
The difference in the absorbing properties between the calibration
source and the sample requires the introduction of an efficiency
correction factor. A method ([15,1995])
which is applicable for any cylindrical
geometry was adapted for the determination of the above
correction factor, using a newly developed experimental-numerical
technique and a Fortran Program. This program using as input the
detector geometry, the source-to-detector distance and the linear
attenuation coefficients µ of both the calibration source and the
material to be analysed, calculates the efficiency correction
factor.

